This is just a guide on how to start, stop, and restart MySQL Server on macOS, Linux, and Windows in case you forgot.
1. On Mac
You can start/stop/restart MySQL Server via the command line.
- For the version of MySQL older than 5.7:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stop sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restart
- For the MySQL version 5.7 and newer:
sudo launchctl load -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plist sudo launchctl unload -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plist
- Or you can turn it on/off via the macOS Preference Panel
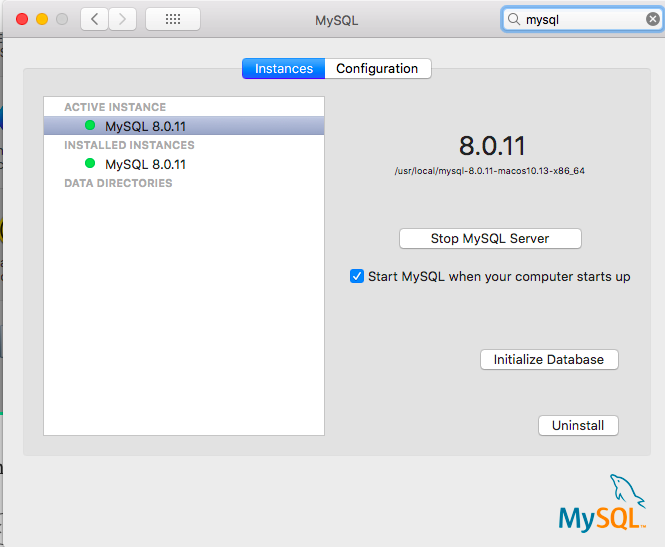
There’s another way which you can use DBngin, an free utility to install and manage multiple database servers on Mac.
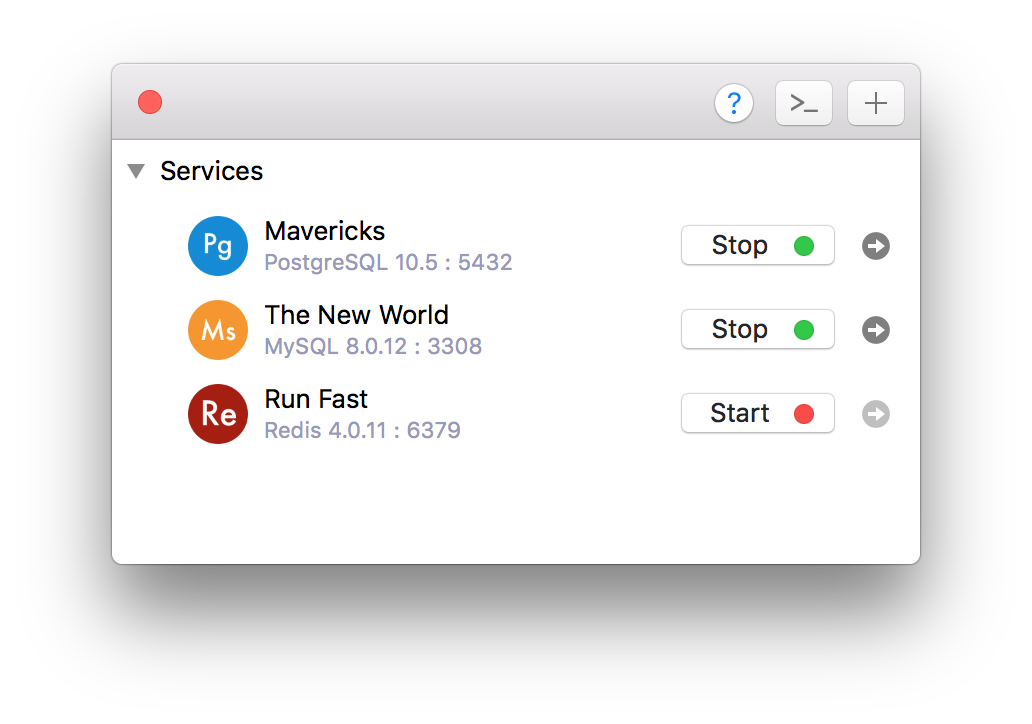
- To turn on/off, it’s just one click away from the server control panel:
2. On Linux
- On Linux start/stop from the command line:
/etc/init.d/mysqld start /etc/init.d/mysqld stop /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
- Some Linux flavours offer the service command too
service mysqld start service mysqld stop service mysqld restart
- or
service mysql start service mysql stop service mysql restart
3. On Windows
- Open Run Window by Winkey + R
- Type services.msc
- Search MySQL service based on version installed.
- Click stop, start or restart the service option.
Or you can start/stop MySQL from the command prompt:
C:> "C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0binmysqld" C:> "C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0binmysqladmin" -u root shutdown
This post was created with our nice and easy submission form. Create your post!


1 Comments
Leave a Reply